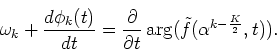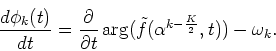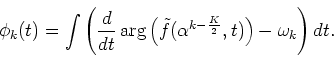Next: Appendix D: Kalman filtering
Up: Bibliography
Previous: Appendix B: Wavelet transform
The wavelet transform in Eq. (21) is a complex representation of the output of the analyzing filter in Eq. (2):
| Xk(t) |
= |
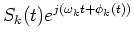 |
|
| |
:= |
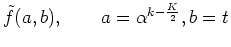 |
(48) |
Taking the absolute value for both terms, we obtain
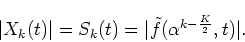 |
(49) |
Similarly, comparing phase terms between Eqs. (48) and (21), we obtain
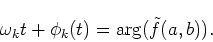 |
(50) |
Since the phase spectrum
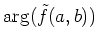 is represented by
is represented by
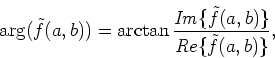 |
(51) |
it becomes a periodical ramp function within
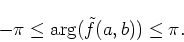 |
(52) |
Differentiating both terms in Eq. (50), we get
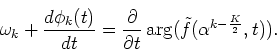 |
(53) |
After clearing, we obtain
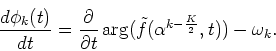 |
(54) |
Hence, the instantaneous output phase 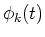 is represented by
is represented by
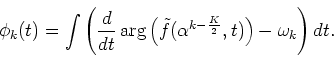 |
(55) |



Next: Appendix D: Kalman filtering
Up: Bibliography
Previous: Appendix B: Wavelet transform
Masashi Unoki
2000-11-07