Research topics
X字型ロボットの車輪型歩容生成と
分離・合体が可能な高機能脚移動システムの開発
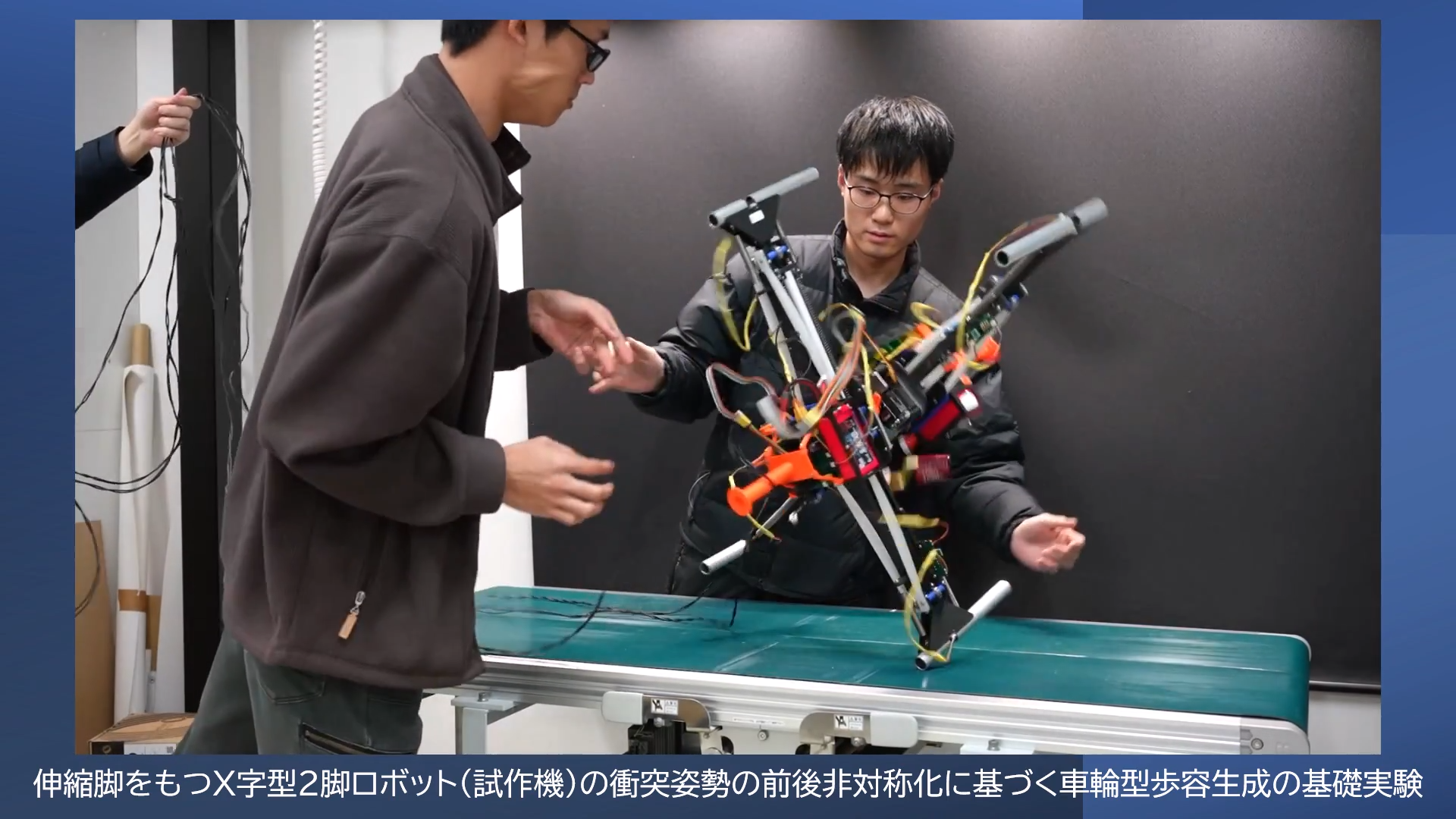
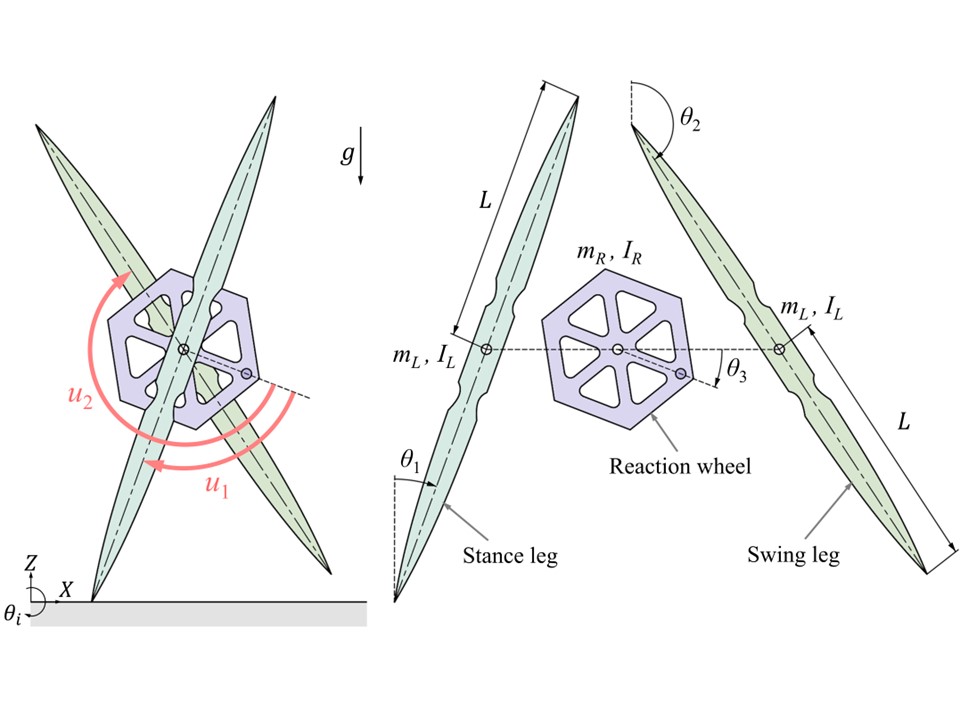
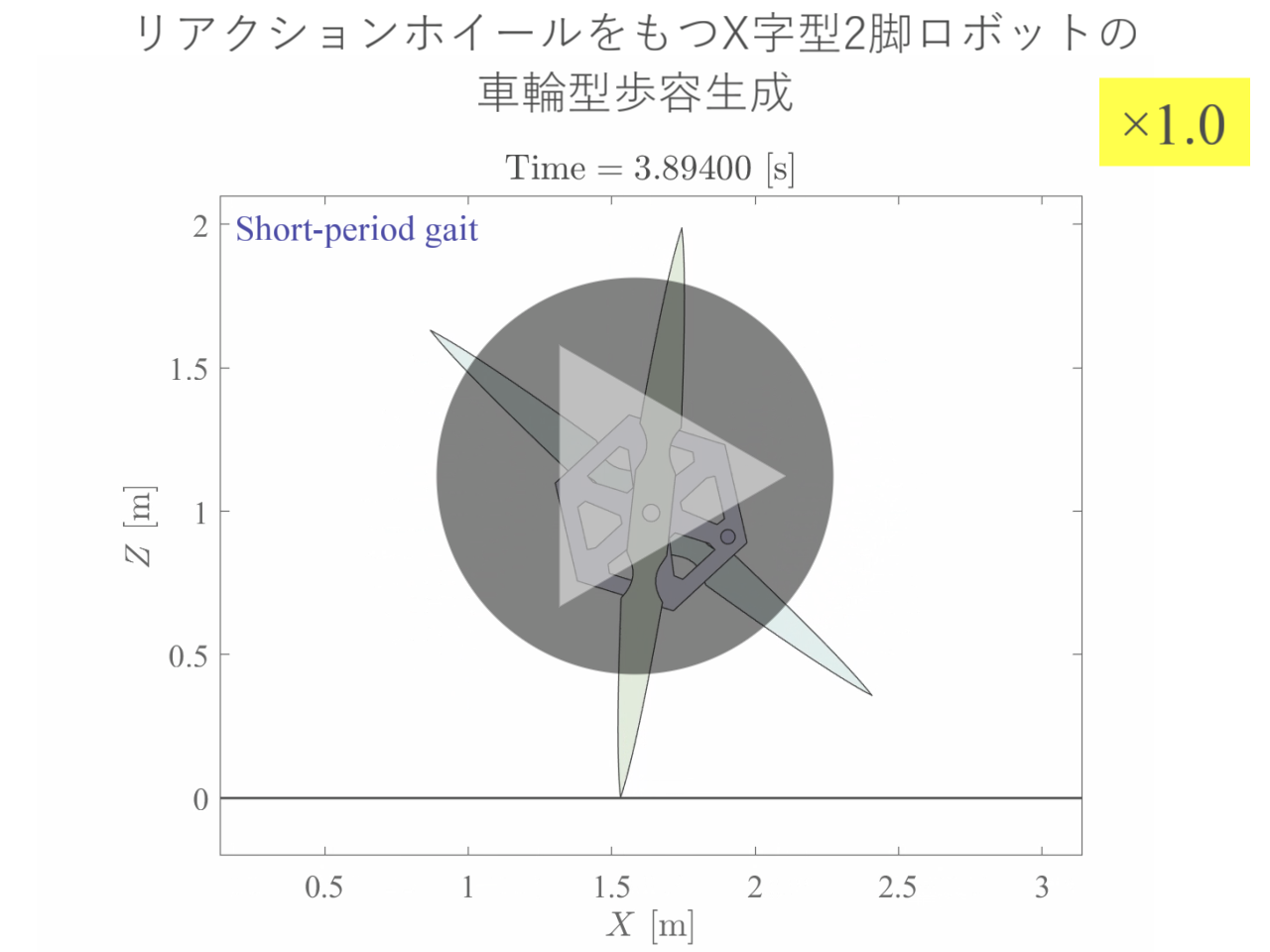
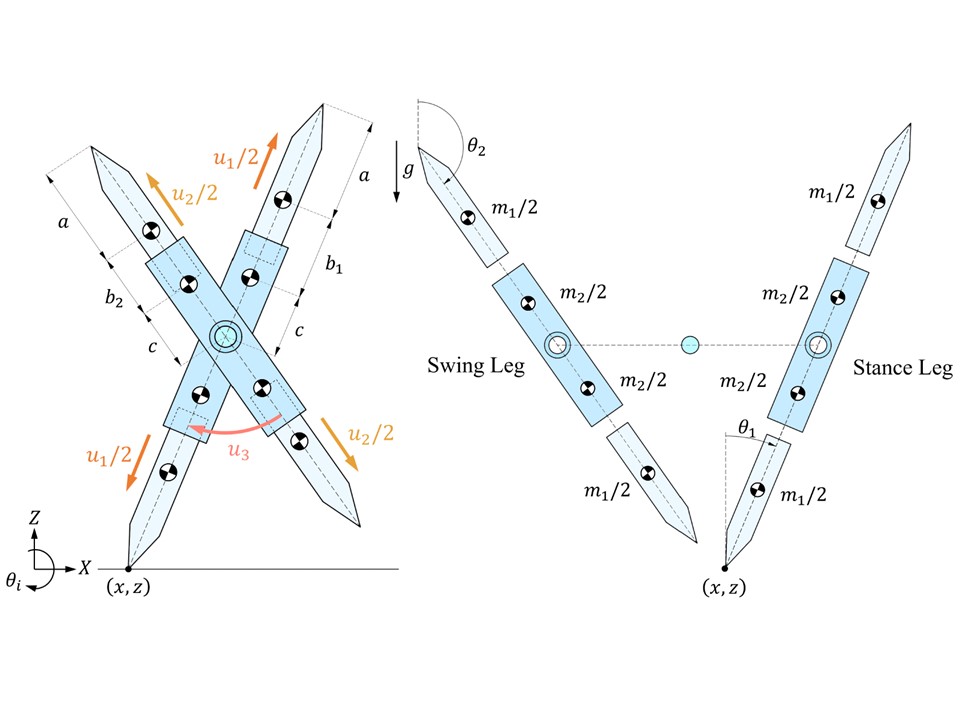
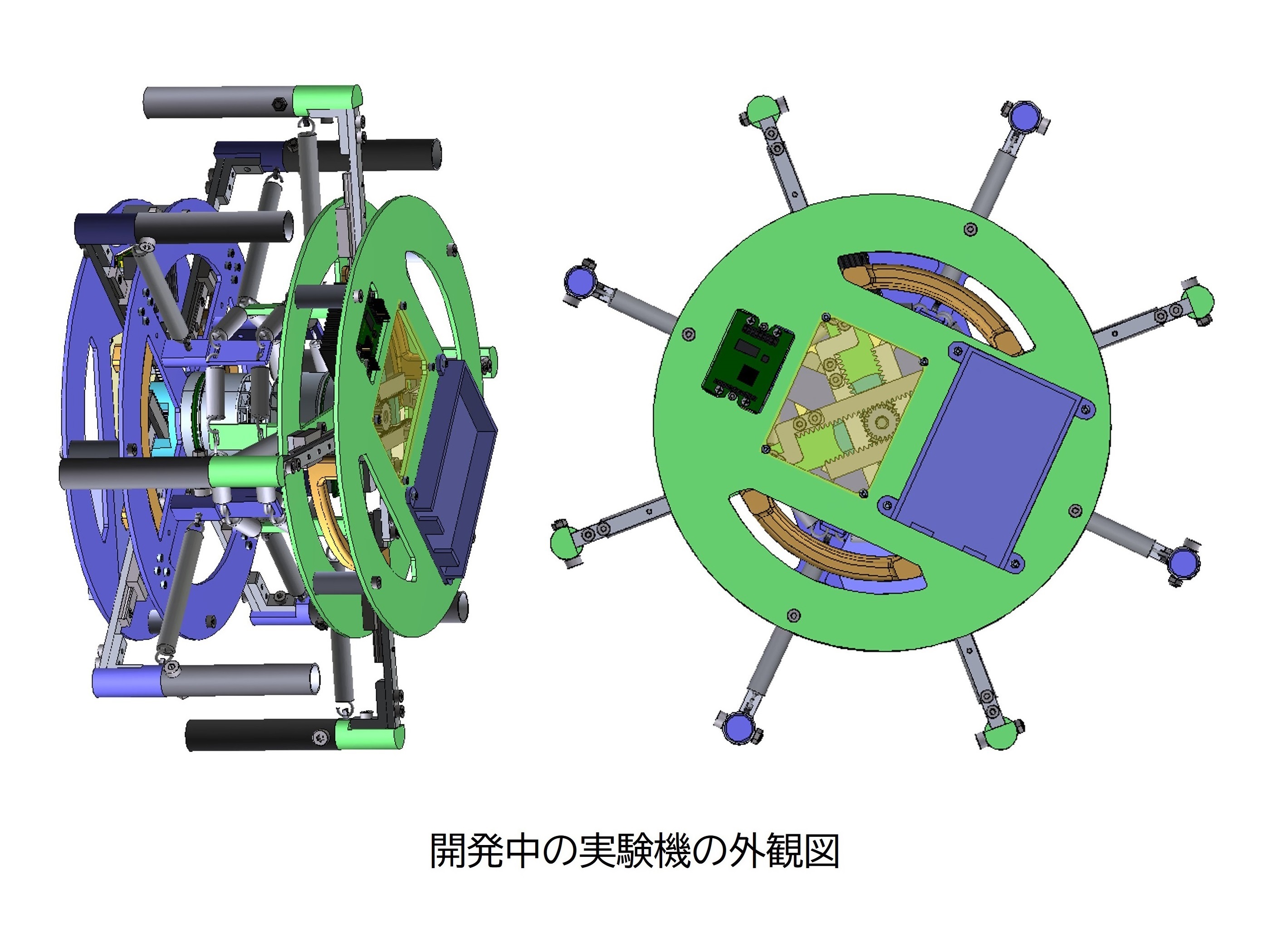
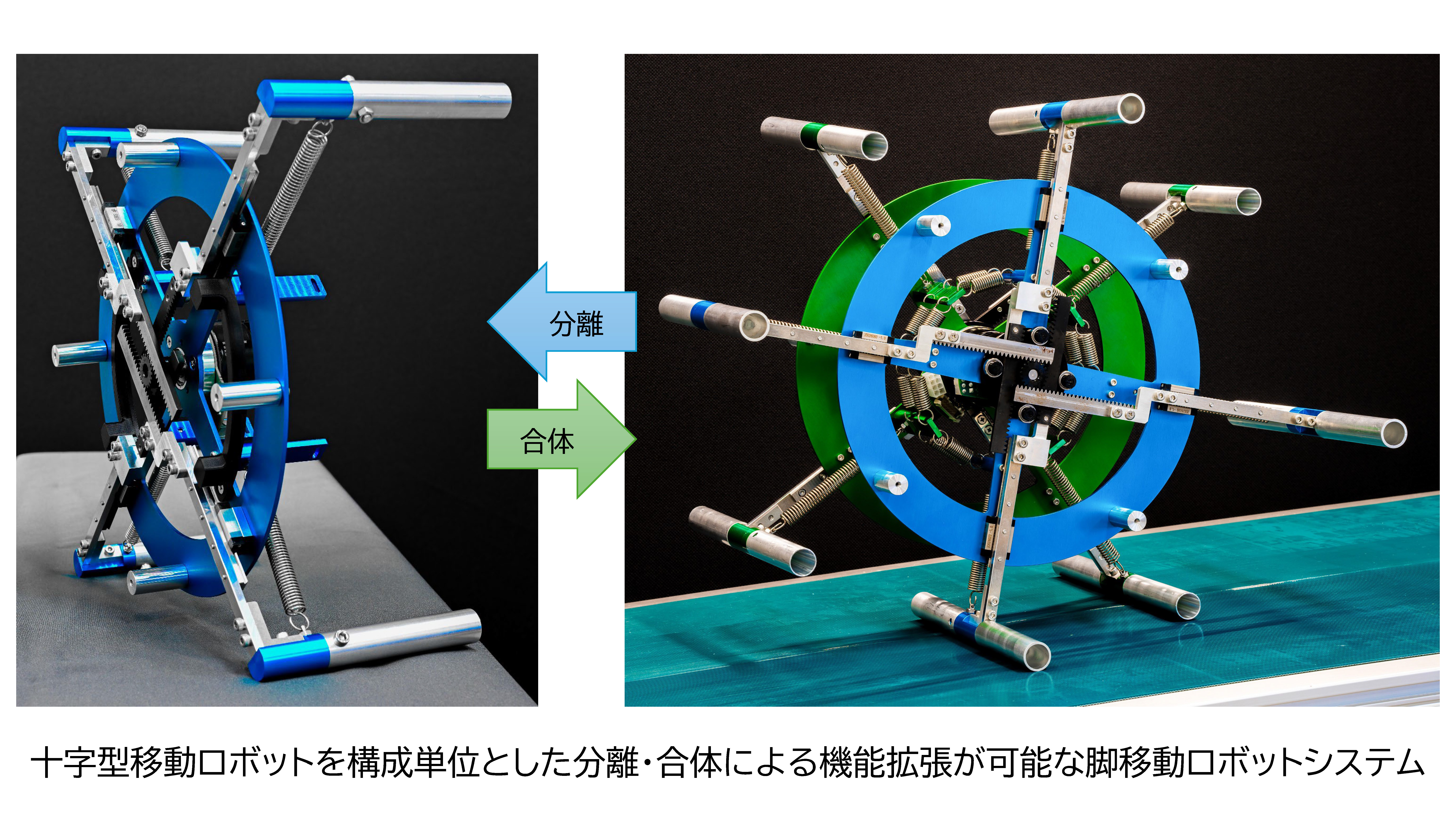
ヒトもロボットも2脚歩行をする場合,単脚支持相において遊脚は支持脚を振り抜く(脚同士が交差する)ように運動します.これに対し私たちの研究室では,遊脚の振り抜き運動が起こらない2脚歩行形態である「車輪型歩容」に着目し,高い環境適応能力をもつ脚移動ロボットの実現に向けた研究を推進しています.車輪型歩容では,支持脚と遊脚が同一方向に回転し,全体としてスポークが転がるような運動となるため,躓く心配がありません.これまでに2本の剛体フレームを重心位置で回転関節を介して接続した「X字型2脚ロボット」を提案し,その車輪型歩容生成のための基礎理論の構築を行ってきました.最近では,水平面上の歩容生成や不整地適応において,より有利であると考えられる伸縮脚を有するX字型2脚ロボットを新たに提案し,衝突姿勢の前後非対称化に基づく高速車輪型歩容生成とその応用に関する研究に取り組んでいます.また,このロボットを構成単位とした分離・合体が可能な多機能脚移動システムの開発も推進しています.
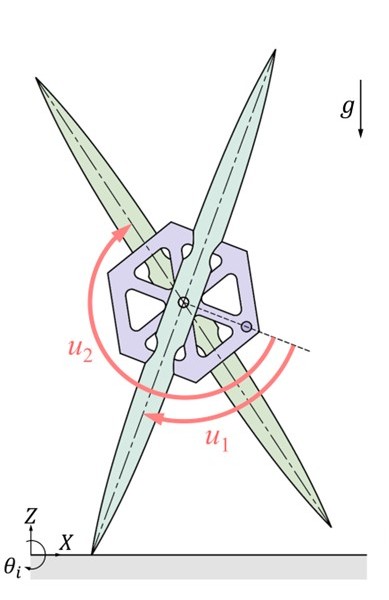
閉鎖の再構成により移動モードの変更が可能な
受動的回転移動ロボット
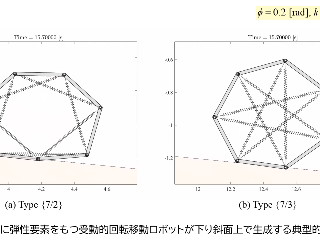
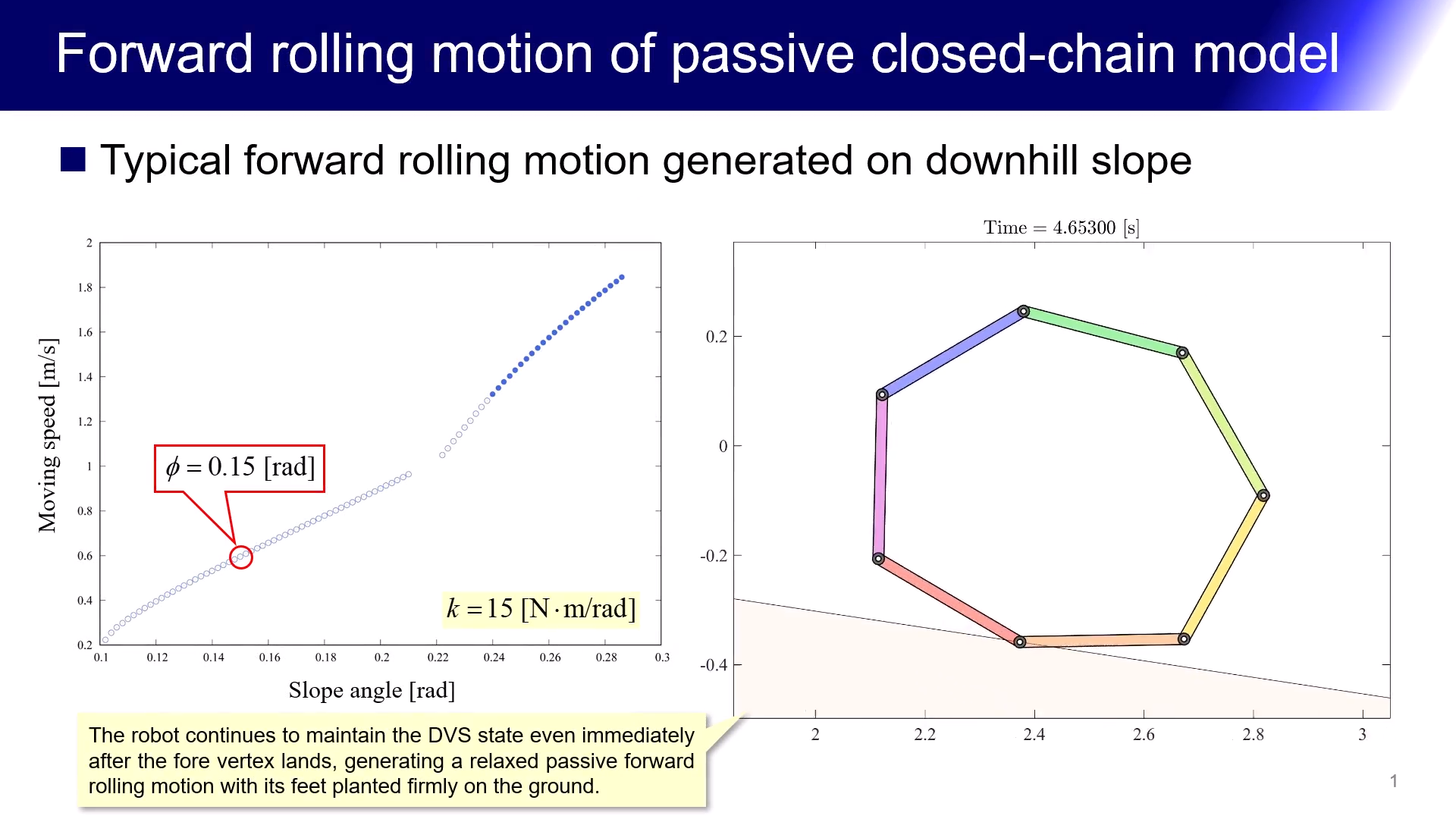
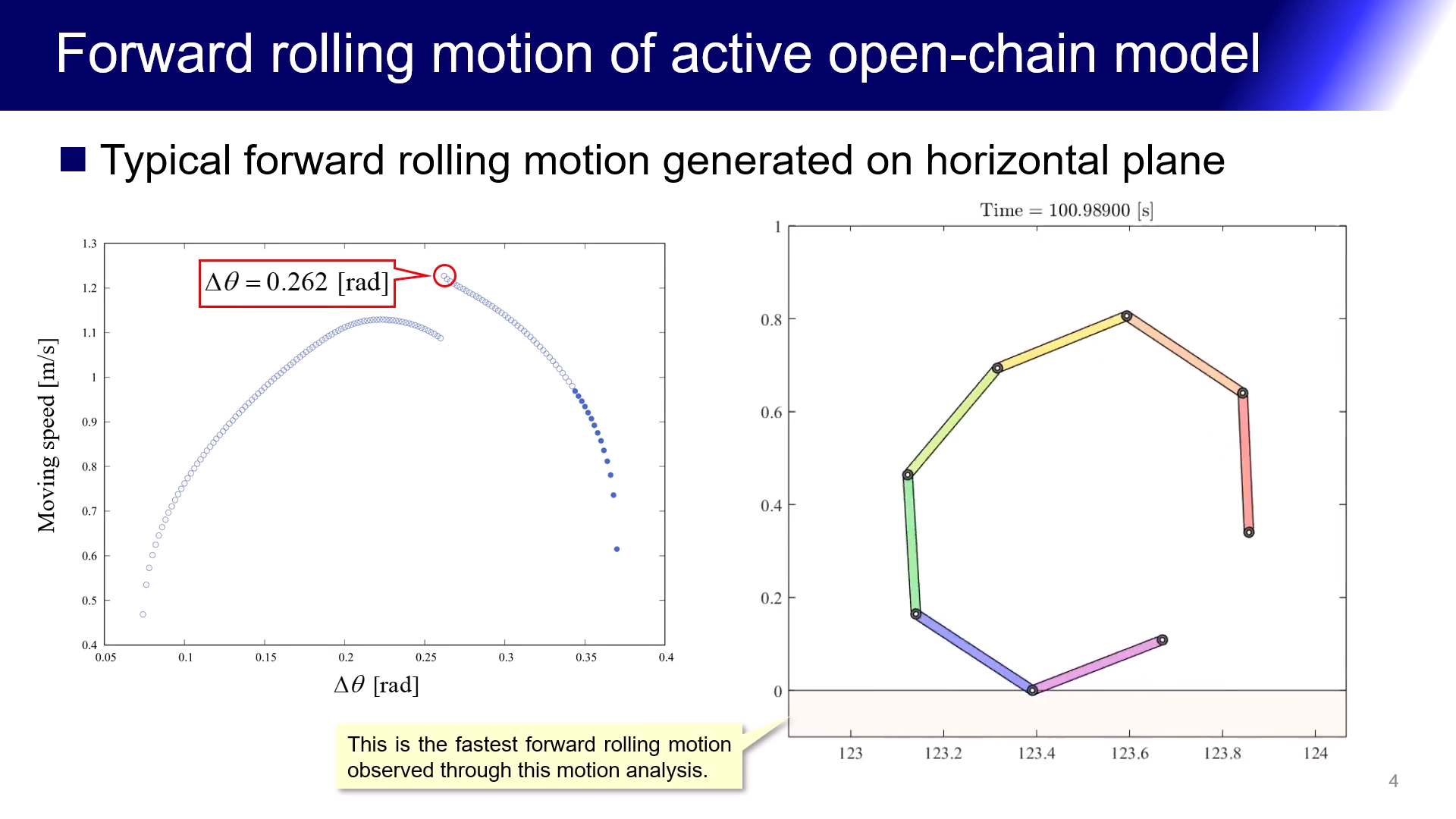
外骨格の頑健さと内部組織の柔軟性を併せもつ七角形状をした受動的回転移動ロボットの研究を推進しています.これは同一の直線状の剛体フレーム7 本を粘弾性をもつ回転関節を介して閉鎖状に結合して凸七角形状の身体を形成したものであり,物理パラメータと初期状態を適切に設定することで緩やかな下り斜面上を重力作用のみを利用して回転移動することが可能です.試作実験器においては,各回転関節に十分な弾性力をもつトーションバネを複数本ずつ取り付けることで,重力下で凸七角形状を維持しながら安定な受動的回転運動を生成することに成功しました.また,トーションバネの代わりに,線形バネを七角形の対角線上に配置(2種類の七芒星形状を構成)しても,安定な受動的回転運動を生成することができました.現在,これらの基本モデルを中心に,内部組織の幾何学的特徴と移動能力との関係について考察を進めています.更に最新の研究により,回転関節の能動化と駆動制御による水平面上の安定な前転運動生成も可能となりました.
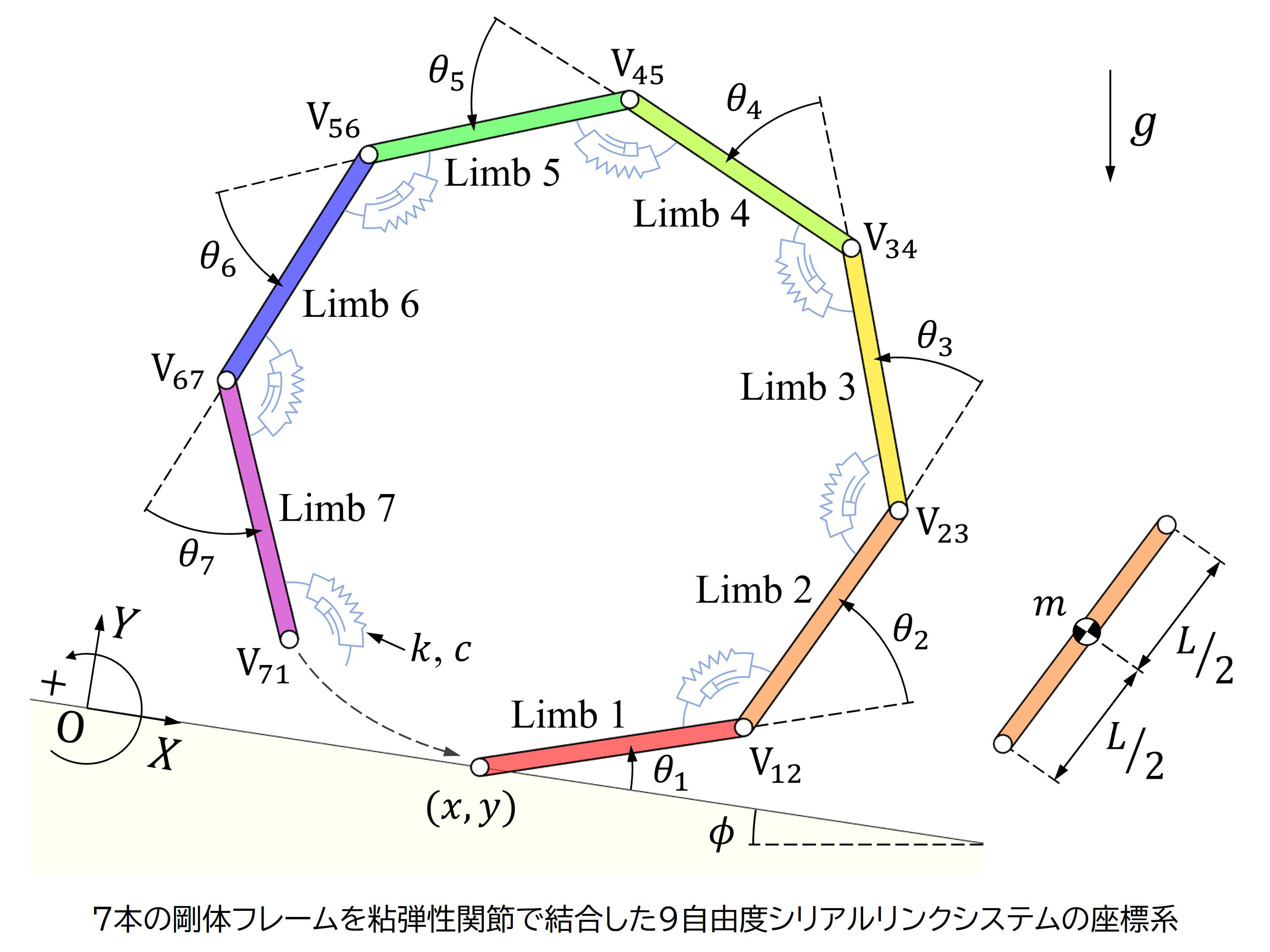

低摩擦路面や急斜面における
安定歩容生成を目指したステルス歩行
滑りやすい路面や急勾配の階段を踏破するには,高効率性を重視したリミットサイクル規範の自然な歩行運動よりも,床面との衝突を回避した緻密で慎重な歩行運動が有利です.本研究室では,足部リンクと足首関節トルクをもたないポイントフットの脚移動ロボットを対象として,前脚着地時の運動エネルギー損失をゼロにする歩行運動(これを忍び足という意味でステルス歩行と呼んでいます)の実現方法とその応用に関する研究に取り組んでいます.特に,支持脚接地点まわりの全角運動量の時間による3階微分をゼロに拘束するように制御することで,床反力の水平方向成分をゼロに保つことができ,摩擦係数がゼロである路面を歩行することも可能となります.現在,低摩擦路面の踏破に有利なロボットの身体構造の考察,およびこれを意識した新しい制御方策の開発を推進しています.
揺動質量が生む力学効果を利用した
劣駆動脚移動ロボットの運動制御
身体内部に十分な数の駆動関節をもたない劣駆動脚移動ロボットの新しい運動制御法として,本体内部の揺動が生む間接励起や引き込みの効果を利用した新しいアプローチを提案しています.本研究室では,写真に示す連結型リムレスホイールを試験機として,その歩行解析を進めています.本体内部の揺動質量の振動にリムレスホイールの歩調が引き込まれると,その歩容の安定性と移動効率は高くなることが明らかにされてきています.引き込み現象が生じる揺動周波数の範囲を拡大するよう,目標時間軌道を最適化することで,エネルギー消費量を一定に保ちながら移動速度の向上を図ることができます.


揺動と摺動を利用した匍匐型移動ロボット
低摩擦路面上をその表面を傷付けることなく安定かつ効率的に移動できる劣駆動ロボットの実現を目指して,凸曲線状の本体フレームの回転・並進運動とその内部で高周波振動をする揺動質量の間接励起の効果を融合した新しい匍匐型運動生成法の考察を進めています.ロボット本体の形状や揺動の目標軌道を最適化することで,緩斜面上だけでなく水平面上においても前進運動生成が可能となることが明らかにされてきています.現在,2台のロボットの連結とその前後揺動の非同期化に基づく前進運動生成身体を構成する基本フレームへの粘弾性要素の追加による高速運動生成など,機能拡張を目指した応用研究にも取り組んでいます.
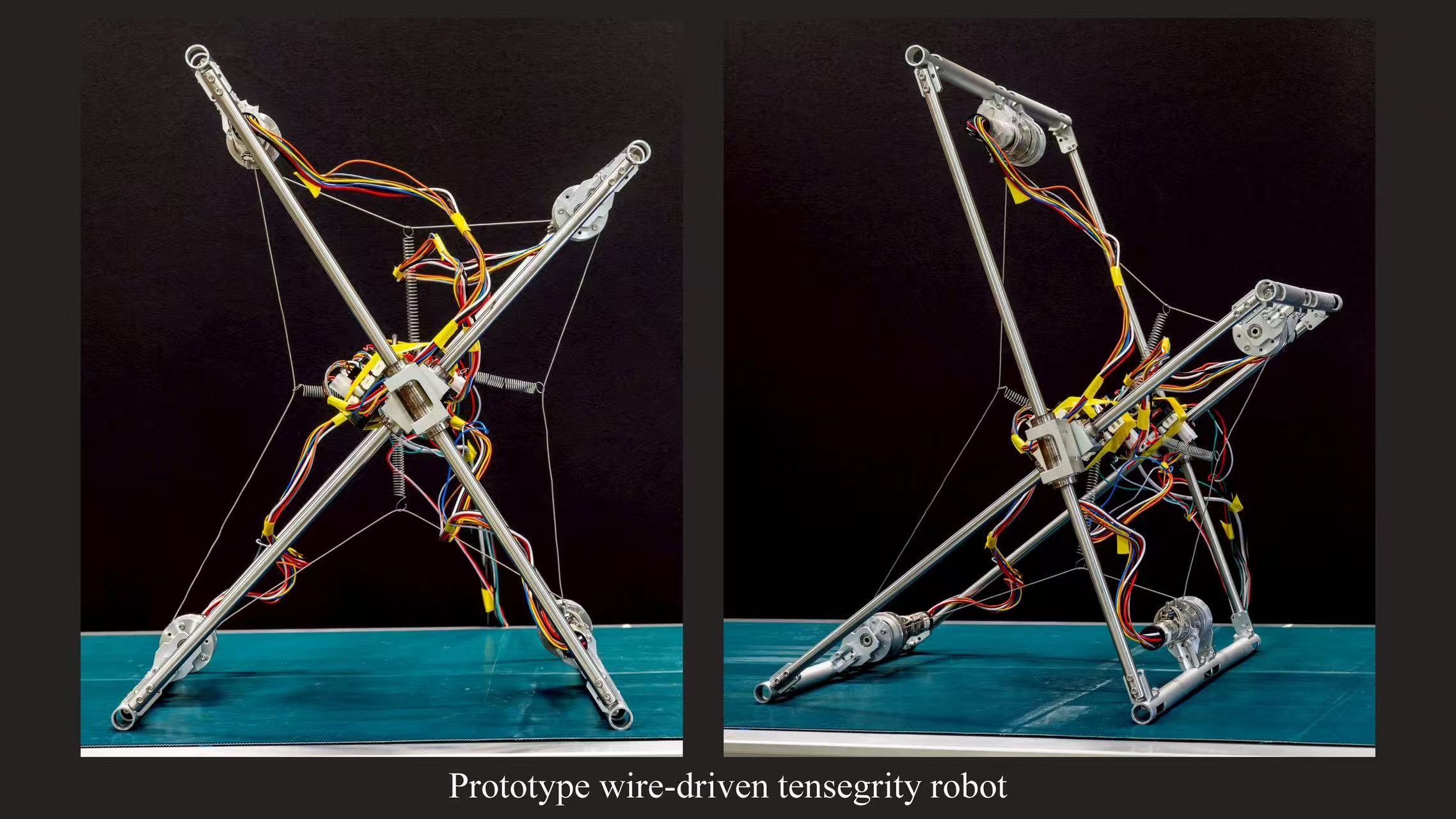
Flexible legged locomotion robot with tensegrity structure
The tensegrity structure, which is widely used in the field of architecture and structural engineering, is a self-supporting and self-stressed spatial grid structure composed of discrete compression elements and continuous tension elements. Accordingly, the tensegrity robots with this kind of structure combines the advantages of rigid robots (high accuracy) and soft robots (high environmental adaptability). Additionally, they conform to morphology and has significant intrinsic compliance, which make them ideal for working in special environments.


Tensegrity spine: a bio-inspired application of tensegrity structures
As an application of the tensegrity structure, a bio-inspired tensegrity spine is proposed in this research. The tensegrity spine is the combination of rigid limbs and elastic elements, which expressed the flexibility of the quadrupeds robot. Specifically, the structure of the tenserity spine can be changed to achive various locomotion characteristics, allows the quadrupeds robot has the capability to adapt a wider range of environments. Additionally, comparing with the past combined rimless wheel connected by rigid rods, at the time of collision occurs, the model with tensegrity spine can store a part of kinetic energy into the elastic element, which can absorb the impact efficiently, demonstrating the great energy utilization.
水上歩行ロボット
水に浮かべた薄い板状の足場の上を駆け抜ける「水上漂」という少林寺の奥義が知られています.本研究室では,これを低弾性路面上の高速歩行運動と捉え,足場と人を抽象化したモデルを導入し,制御系設計と運動解析を進めています.足場の弾性力(復元力)が非常に弱いため,安定な歩行運動を継続するためには,次の足場へ速やかに歩を進め続けなければなりません.しかし単純な高速歩行運動のみならず,床反力やゼロダイナミクスなどの制御も同時に実現しなければならないため,制御系設計は容易ではありません.高速歩容生成とゼロダイナミクスを含めた運動の安定化を同時に達成するためには,ロボットは最低6自由度を有している必要があると考えられます.最近は,足場が存在しない(復元力がゼロである)状況において,脚先に取り付けたフロートが生む浮力や水から受ける抵抗力を利用して,ロボットの身体のみで水上歩行を実現する方法についても検討を進めています.


Ultrahigh-speed strict stealth walking on flexible and zero-friction road surface
Compared to conventional bipedal robots, compass-like bipedal robots were noted to have higher stability and efficiency in walking. Also, it has been pointed out that the simple control makes the underactuated bipedal robot less adaptable to rough surfaces. In response to this, a new walking method called stealth walking has been proposed. In stealth walking, however, the vertical velocity of the tip of the swing leg is controlled to be zero when the swing leg collides with the ground, making it possible to avoid the collision. This increases the stability of the robot and makes it easier to stop the motion. By avoiding impact with the ground, the robot can overcome unstable footholds such as rubble or floating island. Previous research has also shown that a stable walking gait can be achieved at low-friction surfaces by controlling the ground reaction force and angular momentum for constant. Based on those observations, this study focus on achieving high-speed stealth walking on the frictionless vibrating ground by controlling the vertical and horizontal ground reaction forces to improve the adaptability of the bipedal walking robot to adverse environments.