Towards Next-Generation Nanocatalysts to Revolutionize Active Electron Transfer
In a breakthrough, scientists developed a copolymer-conjugated nanocatalytic system, likely paving the way for efficient photoinduced hydrogen generation.
Over the years, scientists have proposed many novel molecular systems for photoinduced electron transfer. In this direction, researchers from Japan have now developed a copolymer-conjugated nanocatalytic system that can drive efficient photoinduced electron transfer. They employed a temperature-responsive ternary random copolymer and coupled it to platinum nanoparticles. By enabling dynamic electron transfer and driving photoinduced hydrogen generation, this innovation can have far-reaching implications for artificial photosynthesis, electrochemical reactions, macromolecular recognition, and bio-inspired soft materials.
Various molecular systems have been developed by researchers for photoinduced (i.e., light-driven) electron transfer, including supramolecules, hybrid materials, and organic polymeric systems. While these systems fulfill the distance criterion required by the electron donor and acceptor for efficient electron transfer, they frequently fall short in accommodating molecular motion, especially in fluid environments. Is there a viable approach to design a system that facilitates electron transfer without succumbing to these limitations?
This issue has been specifically addressed in a recent study. A team of researchers from the Japan Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (JAIST), led by Associate Professor Kosuke Okeyoshi and including Associate Professor Shun Nishimura and Graduate course Student Reina Hagiwara, has now developed a copolymer-conjugated nanocatalytic system to enhance active electron transfer for increased photoinduced hydrogen generation.
Their study, published in Chemical Communications, aims to overcome the limitations of current photoinduced electron transfer systems. The objective of the researchers was to establish an efficient catalyst system capable of promoting electron transfer with only a minimum number of side reactions. Dr. Okeyoshi explains: "This system has potential real-life applications for the hydrogen economy. By integrating the system with an oxygen-generating system, photoinduced water splitting (artificial photosynthesis) is anticipated."
In this regard, viologen is a well-known molecule that is both an efficient electron donor and acceptor. The researchers had previously exploited this property of viologen to develop an electron transfer system, which included the copolymer poly(N-isopropylacrylamide-co-Viologen) (PNV) and modified platinum nanoparticles (Pt NPs). In this system, the temperature-dependent phase transition in PNV responds to viologen's redox changes, allowing for a cyclical electron transfer process for continuous hydrogen generation. However, while the PNVs near the Pt NPs participated in the electron transfer process, free PNV molecules situated farther away could also accept electrons.
To address this issue, the researchers have now designed a copolymer-conjugated nanocatalytic system using the ternary random copolymer poly(NIPAAm-co-Acrylamide-co-Viologen) or PNAV, which was synthesized by precisely controlling the molecular weight and introduction ratio of the polymeric units.
A notable characteristic of PNAV is its temperature-responsive behavior, marked by a phase transition dependent on temperature. This unique copolymer exhibits a discernible shift, oscillating between a swollen state in its oxidized form (PNAV2+) and a shrunken state in its reduced form (PNAV+). Additionally, the connection of PNAV to Pt NPs involves a reduction process, providing control over the distance between the viologen and the Pt NPs. Specifically, the precise swelling/shrinking of PNAV on the Pt NPs proves crucial to the success of the proposed cyclic electron transfer process at a given distance.
The present innovation leverages the advantages of a stimuli-responsive polymer chain to achieve dynamic electron transfer. The copolymer-conjugated nanocatalytic system not only holds promise for facilitating active electron transfer in photoinduced hydrogen generation but also demonstrates potential utility in artificial photosynthetic reactions, such as photoinduced water splitting. Moreover, this innovative approach is anticipated to have broader applications beyond photochemical reactions to encompass various domains, including electrochemical reactions and macromolecular recognition.
The sustainable cyclic electron transfer process enabled by this technology thus presents opportunities for advancements across diverse scientific disciplines. "The long-term implications include the promotion of a hydrogen energy society powered by sunlight and the manufacturing of bio-inspired soft materials as products," concludes Dr. Okeyoshi.
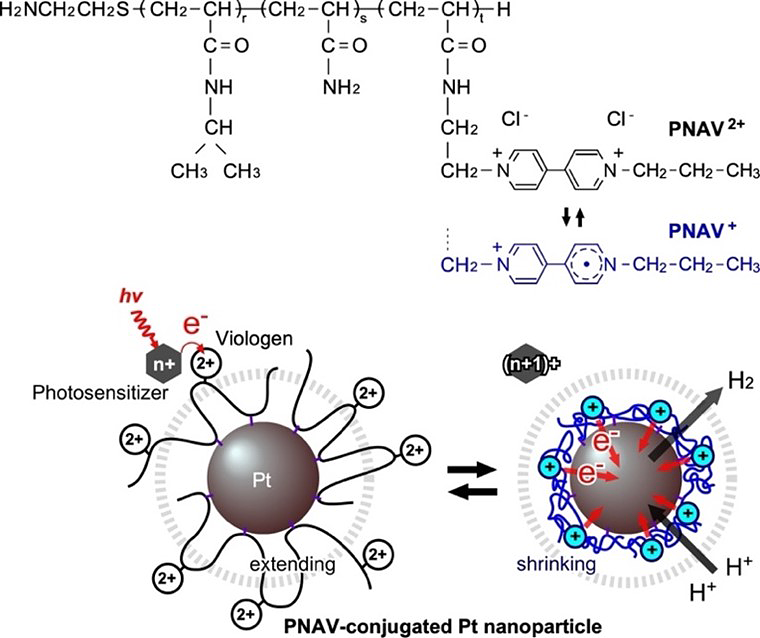
Title: Photoinduced hydrogen generation system employing poly(NIPAAm-co-AAm-co-Viologen) (PNAV)
Caption: The chemical structure and redox states of PNAV, and the electron transfer driven by coil-globule transitions of PNAV conjugated on Pt nanoparticle (NP). The dotted circle represents the effective distance from the Pt NP surface.
Credit: Kosuke Okeyoshi from JAIST
License Type: Original Content
Usage Restrictions: Cannot be reused without permission
Reference
| Title of original paper: | Precise design of copolymer-conjugated nanocatalysts for active electron transfer |
| Authors: | Reina Hagiwara, Shun Nishimura, Kosuke Okeyoshi |
| Journal: | Chemical Communications |
| DOI: | 10.1039/d3cc05242g |
Funding information
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Challenging Research (Exploratory) (Grant number: JP21K18998) from The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT).
December 14, 2023
