


Next: Assumptions and constraints
Up: AUDITORY SEGREGATION MODEL
Previous: AUDITORY SEGREGATION MODEL
First, the observed signal f(t) is decomposed into Sk(t) and  using an auditory-motivated filterbank.
This filterbank is implemented as a constant Q gammatone filterbank, constructed with K=128, bandwidth of 60-6000 Hz, and sampling frequency of 20 kHz [8].
Next, the fundamental frequency F0(t) of the desired signal is determined using an amplitude spectrogram Sk(t)s (see Sec. 3.1).
Then, the concurrent time-frequency region of the desired signal is determined using constraints (i) and (iii) [8].
In the determined concurrent time-frequency region, Ak(t) and Bk(t) are determined from Sk(t),
using an auditory-motivated filterbank.
This filterbank is implemented as a constant Q gammatone filterbank, constructed with K=128, bandwidth of 60-6000 Hz, and sampling frequency of 20 kHz [8].
Next, the fundamental frequency F0(t) of the desired signal is determined using an amplitude spectrogram Sk(t)s (see Sec. 3.1).
Then, the concurrent time-frequency region of the desired signal is determined using constraints (i) and (iii) [8].
In the determined concurrent time-frequency region, Ak(t) and Bk(t) are determined from Sk(t),  ,
,
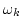 ,
and
,
and
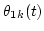 .
Sk(t) and
.
Sk(t) and  are determined by using the amplitude and phase spectra defined by the wavelet transform [8].
are determined by using the amplitude and phase spectra defined by the wavelet transform [8].
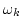 and
and
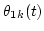 are determined using constraints (ii) and (iv) (see Sec. 2.2 and 3.2).
Finally, f1(t) and f2(t) are determined from Eqs. (
are determined using constraints (ii) and (iv) (see Sec. 2.2 and 3.2).
Finally, f1(t) and f2(t) are determined from Eqs. (![[*]](/usr/share/latex2html/icons.gif/cross_ref_motif.gif) ) and (
) and (![[*]](/usr/share/latex2html/icons.gif/cross_ref_motif.gif) ), respectively.
), respectively.
Table:
Constraints corresponding to Bregman's psychoacoustical heuristic regularities.
| Regularity |
Constraint |
| (i) common onset/offset |
synchronous of onset/offset |
| (ii) gradualness of change |
piecewise-differentiable |
| |
polynomial approximation |
| (slowness) |
(Kalman filtering) |
| (smoothness) |
(spline interpolation) |
| (iii) harmonicity |
multiples of the |
| |
fundamental frequency |
| (iv) changes occurring in |
correlation between the |
| the acoustic event |
instantaneous amplitudes |
|



Next: Assumptions and constraints
Up: AUDITORY SEGREGATION MODEL
Previous: AUDITORY SEGREGATION MODEL
Masashi Unoki
2000-10-26
 using an auditory-motivated filterbank.
This filterbank is implemented as a constant Q gammatone filterbank, constructed with K=128, bandwidth of 60-6000 Hz, and sampling frequency of 20 kHz [8].
Next, the fundamental frequency F0(t) of the desired signal is determined using an amplitude spectrogram Sk(t)s (see Sec. 3.1).
Then, the concurrent time-frequency region of the desired signal is determined using constraints (i) and (iii) [8].
In the determined concurrent time-frequency region, Ak(t) and Bk(t) are determined from Sk(t),
using an auditory-motivated filterbank.
This filterbank is implemented as a constant Q gammatone filterbank, constructed with K=128, bandwidth of 60-6000 Hz, and sampling frequency of 20 kHz [8].
Next, the fundamental frequency F0(t) of the desired signal is determined using an amplitude spectrogram Sk(t)s (see Sec. 3.1).
Then, the concurrent time-frequency region of the desired signal is determined using constraints (i) and (iii) [8].
In the determined concurrent time-frequency region, Ak(t) and Bk(t) are determined from Sk(t),  ,
,
 are determined by using the amplitude and phase spectra defined by the wavelet transform [8].
are determined by using the amplitude and phase spectra defined by the wavelet transform [8].